Euler System of Gas Dynamics
[1]:
try:
import dune.femdg
except ImportError:
print("This example needs 'dune.femdg' - skipping")
import sys
sys.exit(0)
import numpy
from matplotlib import pyplot
from ufl import *
from dune.grid import structuredGrid, reader
import dune.fem
import dune.ufl
from dune.fem.space import dgonb, finiteVolume
from dune.fem.function import gridFunction
from dune.femdg import femDGOperator
from dune.femdg.rk import femdgStepper
from dune.fem.utility import lineSample
dune.fem.threading.use = 4
The dune-fem-dg module can either used stabilizer DG methods to solve this type of problem or higher order FV methods based on linear reconstruction. The following function uses a finite-volume space when order=0 and a dg space with orthonormal polynomials otherwise. Note that when a limiter is then used in the scheme, the finite-volume scheme will use linear reconstruction:
[2]:
def getSpace( gv, order ):
return finiteVolume( gridView, dimRange=4 ) if order==0 else\
dgonb( gridView, dimRange=4, order=order )
Basic model for hyperbolic conservation law
[3]:
class Model:
gamma = 1.4
# helper function
def toPrim(U):
v = as_vector( [U[i]/U[0] for i in range(1,3)] )
kin = dot(v,v) * U[0] / 2
pressure = (Model.gamma-1)*(U[3]-kin)
return U[0], v, pressure
# interface methods for model
def F_c(t,x,U):
rho, v, p = Model.toPrim(U)
return as_matrix( [
[rho*v[0], rho*v[1]],
[rho*v[0]*v[0] + p, rho*v[0]*v[1]],
[rho*v[0]*v[1], rho*v[1]*v[1] + p],
[(U[3]+p)*v[0], (U[3]+p)*v[1]] ] )
# simple 'outflow' boundary conditions on all boundaries
boundary = {range(1,5): lambda t,x,U: U}
# interface method needed for LLF and time step control
def maxWaveSpeed(t,x,U,n):
rho, v, p = Model.toPrim(U)
return abs(dot(v,n)) + sqrt(Model.gamma*p/rho)
Add methods for limiting
[4]:
def velocity(t,x,U):
_, v ,_ = Model.toPrim(U)
return v
def physical(t,x,U):
rho, _, p = Model.toPrim(U)
return conditional( rho>1e-8, conditional( p>1e-8 , 1, 0 ), 0 )
def jump(t,x,U,V):
_,_, pL = Model.toPrim(U)
_,_, pR = Model.toPrim(V)
return (pL - pR)/(0.5*(pL + pR))
Model.velocity = velocity
Model.physical = physical
Model.jump = jump
Method to evolve the solution in time
[5]:
def evolve(space, u_h, limiter="MinMod"):
lu_h = u_h.localFunction()
@gridFunction(space.gridView,name="rho",order=space.order)
def rho(e,x):
lu_h.bind(e)
return lu_h(x)[0]
operator = femDGOperator(Model, space, limiter=limiter) # note: that u_h.space fails since not ufl_space
stepper = femdgStepper(order=space.order+1 if space.order>0 else 2, operator=operator)
operator.applyLimiter(u_h)
t = 0
saveStep = 0.1
fig = pyplot.figure(figsize=(30,10))
rho.plot(gridLines="white", figure=(fig, 131), colorbar=False, clim=[0.125,1])
c = 1
while t <= 0.3:
operator.setTime(t)
t += stepper(u_h)
if t > saveStep:
print(t)
saveStep += 0.1
rho.plot(gridLines="white", figure=(fig, 131+c), colorbar=False, clim=[0.125,1])
c += 1
res = numpy.zeros((2,space.gridView.size(0)))
for i,e in enumerate(space.gridView.elements):
x = e.geometry.center
res[0][i] = x.two_norm
res[1][i] = rho(e,e.geometry.toLocal(x))
return res
A radial Riemann problem
[6]:
x = SpatialCoordinate(dune.ufl.domain(2))
initial = conditional(dot(x,x)<0.1,as_vector([1,0,0,2.5]),
as_vector([0.125,0,0,0.25]))
domain = (reader.dgf, "triangle.dgf")
We start with a triangular grid
[7]:
from dune.alugrid import aluSimplexGrid as simplexGrid
gridView = simplexGrid( domain, dimgrid=2 )
gridView.plot()
# fix the order to use and storage structure for results
res = {}
order = 1
space = getSpace( gridView, order )
Initial conditions for a radial Riemann problem
First solved on a triangle grid and minmod limiter
[8]:
u_h = space.interpolate( initial, name="solution")
res["simplex (minmod)"] = evolve(space,u_h)
femDGOperator: Limiter = MinMod
0.10067226533061213
0.20011688589049687
0.3006285980734703
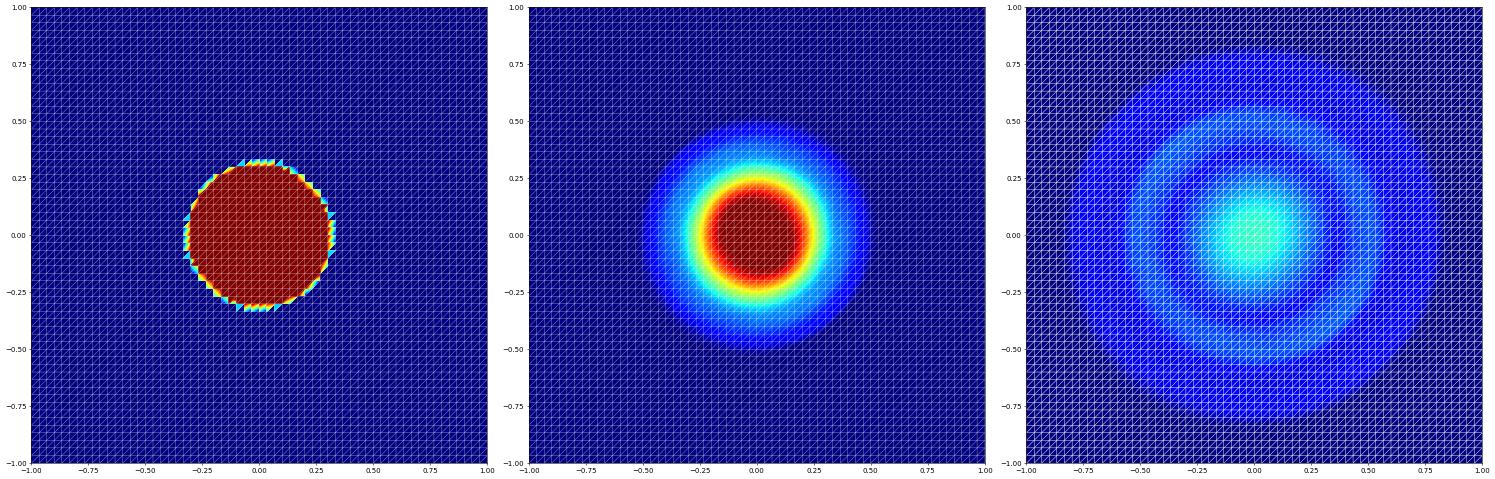
Now a triangle grid without limiter (which of course fails)
[9]:
try:
u_h = space.interpolate( initial, name="solution")
evolve(space,u_h,limiter=None)
except ValueError:
print("SOLUTION NOT VALID")
femDGOperator: Limiter = unlimited
8.089619106880421e+307
SOLUTION NOT VALID
Now a finite volume method first without reconstruction on the triangle grid
[10]:
fvspace = getSpace( gridView, 0 )
u_h = fvspace.interpolate( initial, name="solution")
res["simplex (fv)"] = evolve(fvspace,u_h,limiter=None)
femDGOperator: Limiter = unlimited
0.10210605133997673
0.20082317461244167
0.30230727763246446
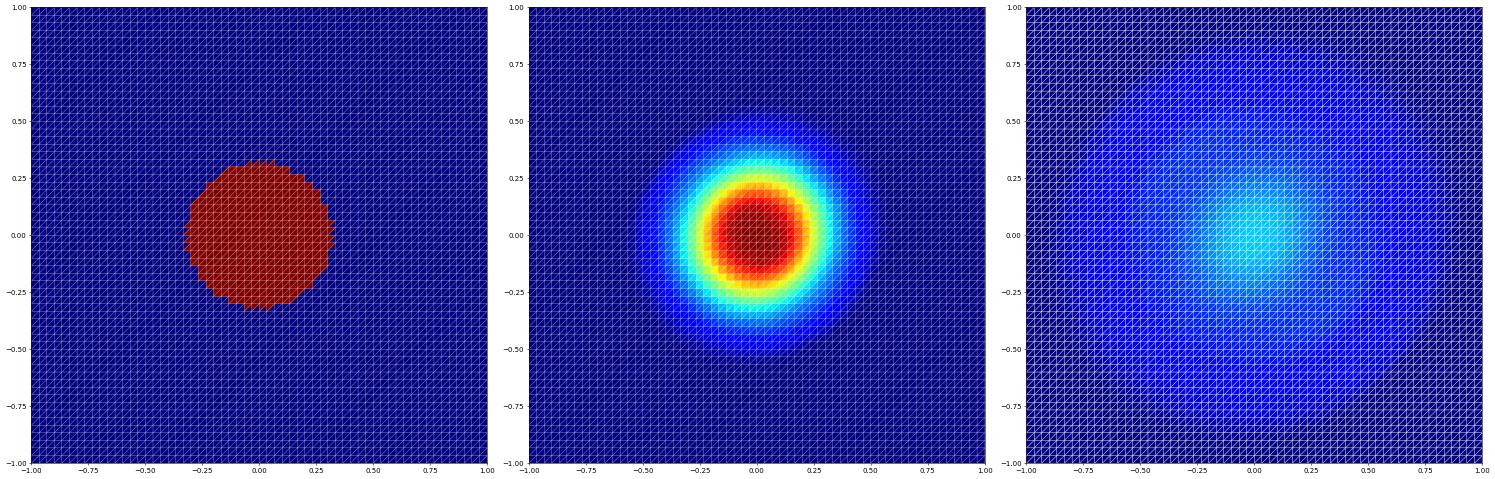
and a finite volume method with reconstruction
[11]:
fvspace = getSpace( gridView, 0 )
u_h = fvspace.interpolate( initial, name="solution")
res["simplex (higher order fv)"] = evolve(fvspace,u_h,limiter="MinMod")
femDGOperator: Limiter = MinMod
0.10084269417709438
0.2019004406055368
0.30190270811495373
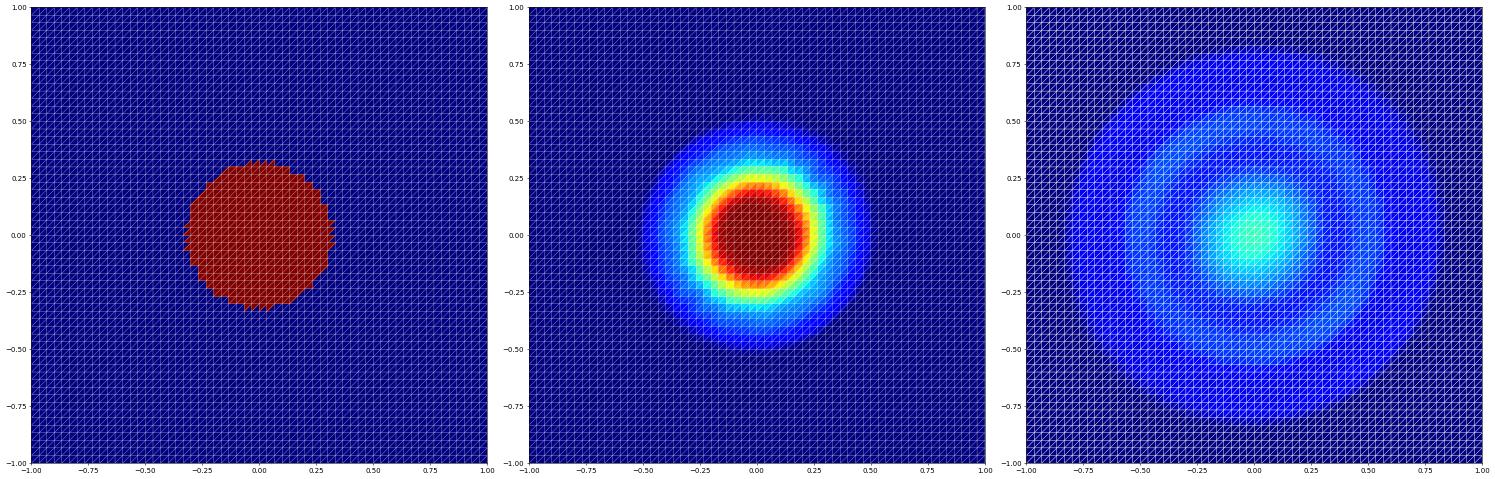
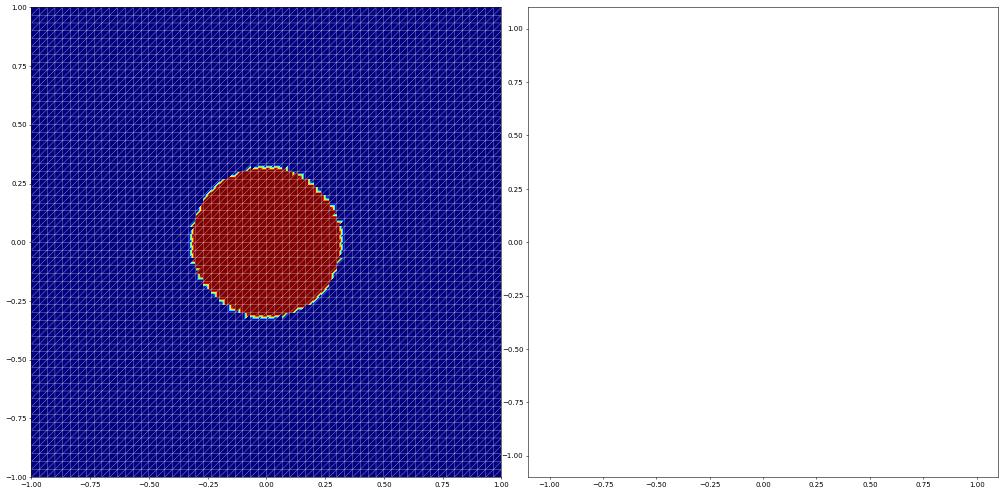
Using a polygonal grid (dual grid of previous grid)
[12]:
try:
from dune.polygongrid import polygonGrid
gridView = polygonGrid( domain, dualGrid=True )
except ImportError:
print("dune.polygongrid module not found using the simplex grid again")
gridView = simplexGrid( domain, dimgrid=2 )
gridView.plot()
space = getSpace( gridView, order )
dune.polygongrid module not found using the simplex grid again
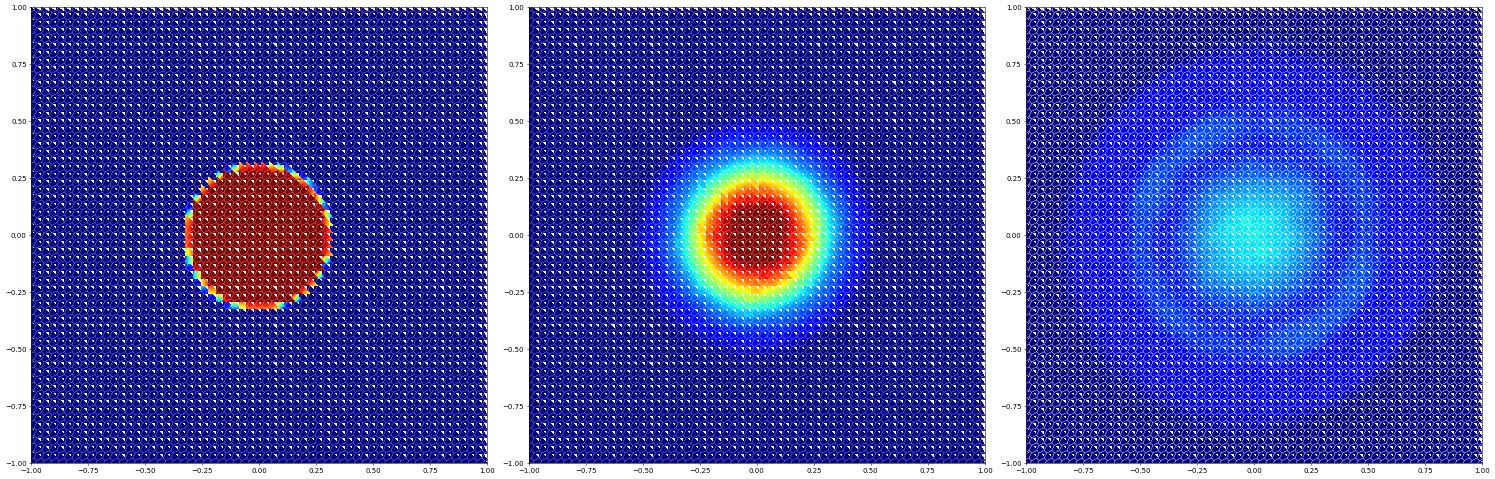
Solution with limiter - fails as above without
[13]:
u_h = space.interpolate( initial, name="solution")
res["polygons (minmod)"] = evolve(space,u_h)
femDGOperator: Limiter = MinMod
0.10067226533061213
0.20011688589049687
0.3006285980734703
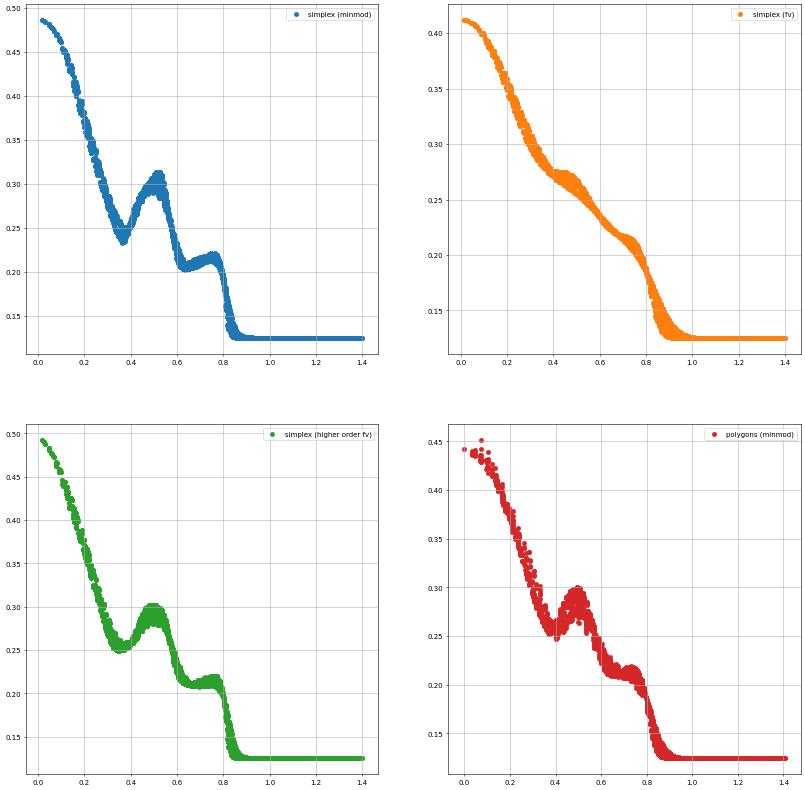
Solutions along the diagonal
[14]:
color = ['tab:blue', 'tab:orange', 'tab:green', 'tab:red']
figure = pyplot.figure(figsize=(20,20))
for i,(k,x) in enumerate(res.items()):
ax = pyplot.subplot(221+i)
ax.scatter(x[0],x[1], color=color[i], label=k)
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
pyplot.show()