Dune Core Modules (2.5.0)
Classes | |
| struct | Dune::ReferenceElements< ctype, dim > |
| Class providing access to the singletons of the reference elements. More... | |
| class | Dune::ReferenceElement< ctype, dim > |
| This class provides access to geometric and topological properties of a reference element. More... | |
Detailed Description
Generic Geometries
Introduction
In the following we will give a definition of reference elements and subelement numbering. This is used to define geometries by prescribing a set of points in the space \mathbf{R}^w .
The basic building block for these elements is given by a recursion formula which assigns to each set E \subset \mathbf{R}^d either a prism element E^\vert\subset \mathbf{R}^{d+1} or a pyramid element E^\circ\subset \mathbf{R}^{d+1} with E^\vert = \lbrace (x,\bar{x}) \mid x \in E, \bar{x} \in [0,1] \rbrace and E^\circ = \lbrace ((1-\bar{x})x,\bar{x}) \mid x \in E, \bar{x} \in [0,1] \rbrace . The recursion starts with a single point P_0=0\in\mathbf{R}^0 .
For d=1,2,3 this leads to the following elements
- d=1 : L_1 = P_0^\vert = P_0^\circ = [0,1] is a line.
- d=2 : Q_2 = L_1^\vert is a cube and S_2 = L_1^\circ is a simplex.
- d=3 : Q_3 = Q_2^\vert is a cube, S_3 = S_2^\circ is a simplex, \mathrm{pyramid}_3 = Q_2^\circ is a pyramid, and \mathrm{prism}_3 = S_2^\vert is a prism.
In general if Q_d is a cube then Q_d^\vert is also a cube and if S_d is a simplex then S_d^\circ is also a simplex.
Based on the recursion formula we can also define a numbering of the subentities and also of the sub-subentities of E^\vert or E^\circ based on a numbering of E . For the subentities of codimension c we use the numbering
- E^\vert : the first numbers are assigned to the entities parallel to the x_d-axis in the same order as the subentites of the same codimension in E ; then to the subentities of codimension c-1 in the bottom followed by those in the top.
- E^\circ : in this case we first number the subentities of codimension c-1 in the bottom, followed by each subentity based on a subentity of codimension c in E .
For the subentity of codimension cc in a codimension c subentity E' we use the numbering induced by the numbering the reference element corresponding to E' .
Here is a graphical representation of the reference elements:
- One-dimensional reference element. For d=1 the simplex and cube are identical

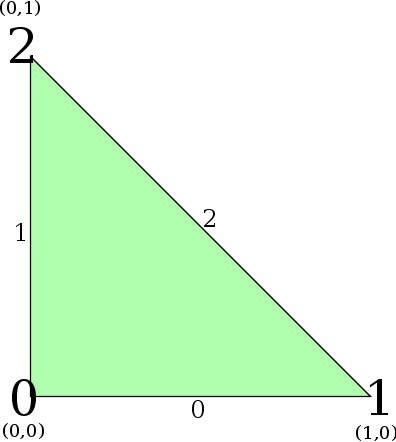
- Two-dimensional reference simplex (a.k.a. triangle)
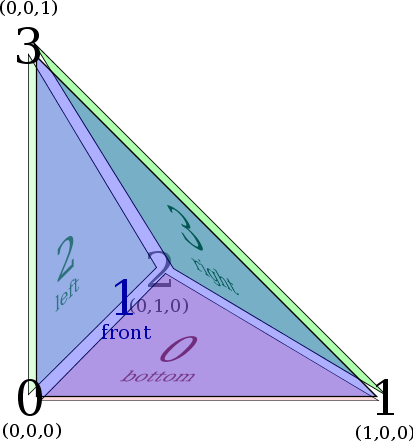
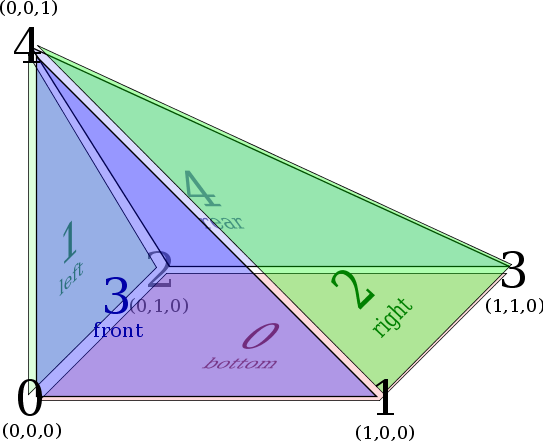
- Three-dimensional reference simplex (a.k.a. tetrahedron)
 Face Numbering
Face Numbering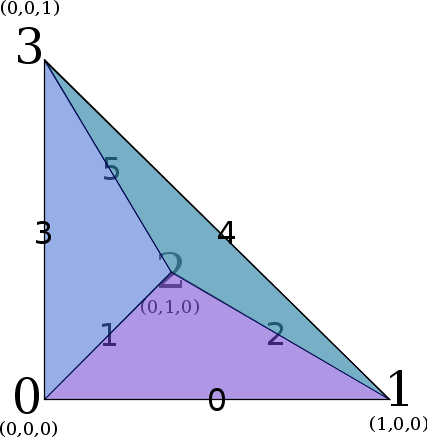 Edge Numbering
Edge Numbering - Two-dimensional reference cube (a.k.a. quadrilateral)
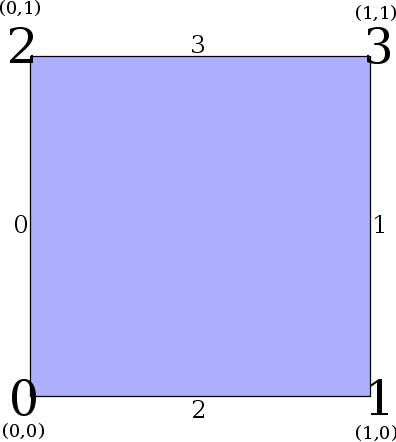
- Three-dimensional reference cube (a.k.a. hexahedron)
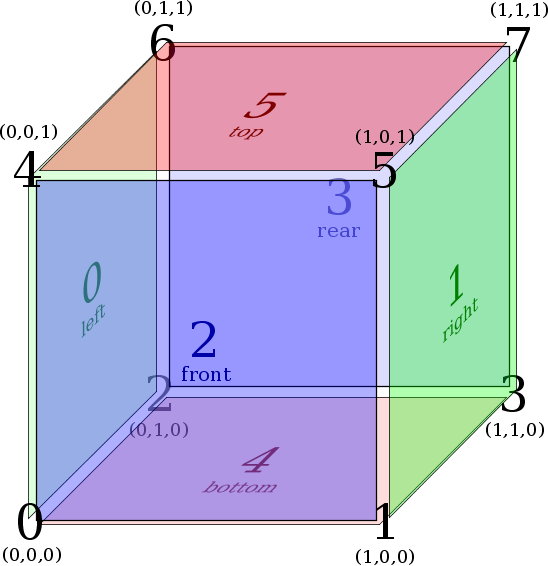 Face Numbering
Face Numbering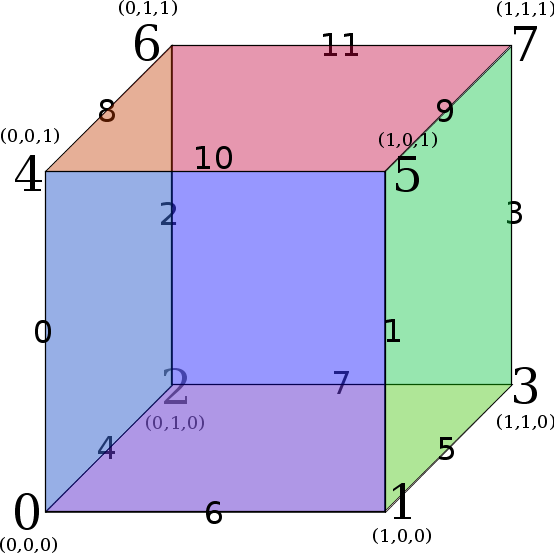 Edge Numbering
Edge Numbering - Prism reference element
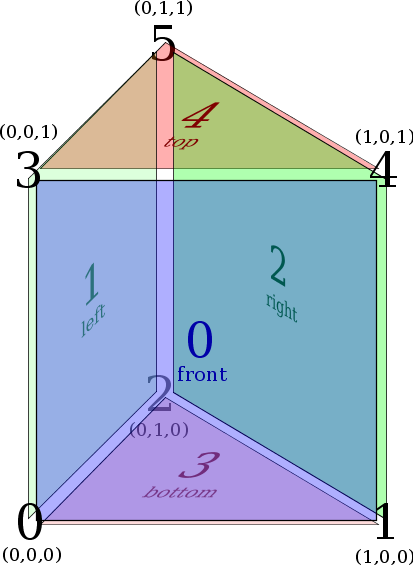 Face Numbering
Face Numbering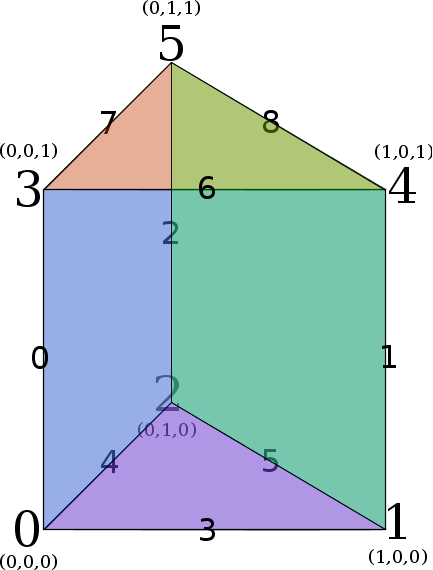 Edge Numbering
Edge Numbering - Pyramid reference element
 Face Numbering
Face Numbering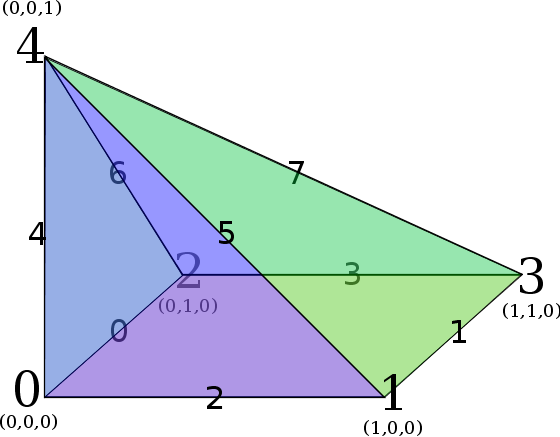 Edge Numbering
Edge Numbering
In addition to the numbering and the corner coordinates of a reference element \hat{E} we also define the barycenters b(\hat{E}) , the volume |\hat{E}| and the normals n_i(\hat{E}) to all codimension one subelements.
The recursion formula is also used to define mappings from reference elements E to general polytop given by a set of coordinates for the corner points - together with the mapping \Phi , the transpose of the Jacobian D\Phi^T(x)\in\mathbf{R}^{d,w} is also defined where d is the dimension of the reference element and w the dimension of the coordinates. This suffices to define other necessary parts of a Dune geometry by LQ-decomposing D\Phi^T : let D\Phi^T(x) = LQ be given with a lower diagonal matrix L\in \mathbf{R}^{d,d} and a matrix Q\in\mathbf{R}^{d,w} which satisfies Q Q^T = I :
- Jacobian inverse transpose
D\Phi(x)^{-T}:=Q^T L^{-1}.
- Integration element
\sqrt{\mathrm{det}(D\Phi(x)^T D\Phi(x))} = \sqrt{\mathrm{det}(LL^T)} = \Pi_{i=1}^d l_{ii}.
- Volume
\int_{\hat{E}} \Pi_{i=1}^d l_{ii}(x) d\;x = |\hat{E}| \Pi_{i=1}^d l_{ii}(b(\hat{E})).
(Here some assumptions on the degree of the integration element is used.)
The next sections describe the details of the construction.
Reference Topology
We define the set \mathcal{T} of reference topologies by the following rules:
- \mathcal{T} contains an element \mathbf{p} that we call the point topology.
- For T \in \mathcal{T}, \mathcal{T} contains an element T^\vert that we call the prism over T.
- For T \in \mathcal{T}, \mathcal{T} contains an element T^\circ that we call the pyramid over T.
For each reference topology T we define the following values:
- Dimension: The point topology has dimension zero and the dimension of a prism or a pyramid topology over t has dimension d(t)+1.
- Size: For c=0,\dots,d with d=d(T) we define the number s_c(T) through
- s_0(T)=1.
- If T=t^\vert then s_d(T)=2s_{d-1}(t) and for c\in \{1,\dots,d-1\} we have s_c(T)=s_{c}(t)+2s_{c-1}(t).
- If T=t^\circ then s_d(T)=s_{d-1}(t)+1 and for c\in \{1,\dots,d-1\} we have s_c(T)=s_{c-1}(t)+s_{c}(t).
- Subtopology: Given a reference topology T of dimension d and a codimension c=0,\dots,d we now define the subtopology S_{c,i}(T)\in\mathcal{T} for i=1,\dots,s_c(T):
- S_{0,1}(T)=T and S_{d,i}(T)=\mathbf{p}
- For T=t^\vert and c\in \{1,\dots,d-1\} we define using the abbreviations p=s_{c}(t),q=s_{c-1}(t)
S_{c,i}(T) = \left\{\begin{array}{ll} S_{c,i}(t)^\vert & \mbox{for}\; i=1,\dots,p, \\ S_{c-1,i-p}(t) & \mbox{for}\; i=p+1,\dots,p+q, \\ S_{c-1,i-p-q}(t) & \mbox{for}\; i=p+q+1,\dots,p+2q. \end{array}\right.
- For T=t^\circ and c\in \{1,\dots,d-1\} we define using the abbreviations p=s_{c}(t),q=s_{c-1}(t)
S_{c,i}(T) = \left\{\begin{array}{ll} S_{c-1,i}(t) & \mbox{for}\; i=1,\dots,q, \\ S_{c,i-q}(t)^\circ & \mbox{for}\; i=q+1,\dots,q+p. \end{array}\right.
Notice that the number of vertices (i.e., subtopologies of codimension d(T)) of a topology T does not uniquely identify the topology. To see this, consider the topologies T_1 = \mathbf{p}^{\vert\vert\vert\circ\circ} and T_2 = \mathbf{p}^{\circ\circ\circ\circ\vert}. For these topologies we have s_d( T_1 ) = s_d( T_2 ) = 10.
Reference Domains
For each reference topology T we assosiate the set of corners \mathcal{C}(T):=(p_i(T))_{1=1}^{s_d(T)}\subset\mathbf{R}^d(T) defined through
- T=\mathbf{p}: p_0(T)=0\in\mathbf{R}^0
- T=t^\vert: p_k(T)=(p_k(t),0),p_{d'+k}(T)=(p_k(t),1) for k=1,\dots,d', with d'=s_d(t).
- T=t^\circ: p_k(T)=(p_k(t),0) for k=1,\dots,d-1 and p_d(T)=e_d with d=s_d(T)
The convex hall of the set of points \mathcal{C}(T) defines the reference domain \mathrm{domain}(T) for the reference topology T; it follows that
- \mathrm{domain}( \mathbf{p} ) := \lbrace 0 \rbrace \subset \mathbf{R}^0,
- \mathrm{domain}( T^\vert ) := \mathrm{domain}( T ) \times [0,1],
- \mathrm{domain}( T^\circ ) := \lbrace ((1-\bar{x})x,\bar{x}) \mid x \in \mathrm{domain}( T ), \bar{x} \in [0,1] \rbrace.
Reference Elements and Mappings
A pair E=(T,\Phi) of a topology T and a map \Phi:\mathrm{domain}( T ) \to \mathbf{R}^w with w\geq d(T) is called an element.
The reference element is the pair E(T)=(T,{\rm id}).
For a given set of points \mathcal{C}:=(p_i)_{1=1}^{s_d(T)}\subset\mathbf{R}^w we define a mapping \Phi_T(\mathcal{C},\cdot)\mathrm{domain}( T ) \to \mathbf{R}^w through \Phi_T(\mathcal{C};p_i(T))=p_i for all p_i(T)\in \mathcal{C}(T). This mapping can be expressed using the recursive definition of the reference topologies through:
- \Phi_{\mathbf{p}}( (p_0) ; x ) = p_0,
- \Phi_{T^\vert}( (p_1,\ldots,p_{s_d(T^\vert)} ; (x,\bar{x}) ) = (1 - \bar{x}) \Phi_T( p_1,\ldots,p_{s_d(T)} ; x ) + \bar{x} \Phi_T( p_{s_d(T)+1},\dots,p_{s_d(T^\vert)} ; x ) with x\in \mathrm{domain}( T ) and \bar{x}\in[0,1].
- \Phi_{T^\circ}( p_1,\ldots,p_{s_d(T^\circ)}) ; (x,\bar{x}) ) = (1 - \bar{x}) \Phi_T( p_1,\ldots,p_{s_d(T)-1} ; x ) + \bar{x} p_{s_d(T^\circ)} with x\in \mathrm{domain}( T ) and \bar{x}\in[0,1].
Numbering of Subelements
Given a reference topology T, a codimension c\in\{0,\dots,d(T)\} and a subtopology S_{c,i}(T) we define a subset of the corner set \mathcal{C}(T) \mathcal{C}_{c,i}(T)= (p_{k_j}(T))_{j=1}^{s_{d(S_{c,i}(T)}(S_{c,i}(T))} given by the subsequence \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_j)_{j=1}^{s_{d(S_{c,i}(T)}(S_{c,i}(T))} of \{1,dots,s_{d(T)}(T)\} :
\mathcal{C}_{0,0}(T) = \mathcal{C}(T), \mathcal{C}_{d(T),i}(T) = (p_i(T)) , and for c\in\{1,\dots,d(T)-1\} we define \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_j)_{j=1}^{s_{d(S_{c,i}(T)}(S_{c,i}(T))} through the recursion
- T=t^\vert:
For i=1,\dots,s_c(T) we define \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_1,\dots,k_n, k_1+s_{d(t)}(t)\dots,k_n+s_{d(t)}(t)) with \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)= \{k_1,\dots,k_n\} .
For i=s_(T)+1,\dots,s_c(T)+s_{c+1}(T) we define \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_1,\dots,k_n) with \mathcal{K}_{c-1,i}(T)= \{k_1,\dots,k_n\} .
For i=s_c(T)+s_{c+1}(T)+1,\dots,s_c(T)+2s_{c+1}(T) we define \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_1+s_{d(t)}(t),\dots,k_n+s_{d(t)}(t)) with \mathcal{K}_{c-1,i}(T)= \{k_1,\dots,k_n\} . - T=t^\circ:
For i=1,\dots,s_{c-1}(T) we define \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_1,\dots,k_n) with \mathcal{K}_{c-1,i}(T)= \{k_1,\dots,k_n\} .
For i=s_{c-1}(T)+1,\dots,s_{c-1}(T)+s_c(T) we define \mathcal{K}_{c,i}(T)=(k_1,\dots,k_n,s_{d(T)}(T)) with \mathcal{K}_{c-1,i}(T)= \{k_1,\dots,k_n\} .
Given these subsets we define subreference elements E_{c,i}(T)=(S_{c,i}(T),\Phi_{c,i}(T)) of E(T) given by the following mapping \Phi_{c,i}(T,\cdot)=\Phi(S_{c,i}(T),\mathcal{C}_{c,i}(T),\cdot) .
Furthermore we define a numbering of the subreference elements of each subreference element in T. This is the number k=\mathrm{index}_{c,i,cc,ii}(T) for c\in\{0,\dots,d(T)\}, i\in\{1,\dots,s_c(T)\} , and cc\in\{0,\dots,d(S_{c,i})\}, ii\in\{1,\dots,s_{cc}(S_{c,i})\} for which
\Phi_{c,i}(S_{c,i}(T))\circ \Phi_{cc,ii}(S_{cc,ii}(S_{c,i}(T))) = \Phi_{c+cc,k}(T).
 |
Legal Statements / Impressum |
Hosted by TU Dresden & Uni Heidelberg |
generated with Hugo v0.111.3
(Apr 9, 22:44, 2025)
|
Legal Statements / Impressum |
Hosted by TU Dresden & Uni Heidelberg |
generated with Hugo v0.111.3
(Apr 9, 22:44, 2025)